8
toll free 800.334.5214 ACME ELECTRIC |
hubbell-acmeelectric.comQ u e s t i o n s a n d A n s w e r s
16. Is one insulation systembetter than another?
Not necessarily. It depends on the application and the cost benefit to be realized. Higher temperature class insulation systems
cost more and larger transformers are more expensive to build. Therefore, the more expensive insulation systems are more
likely to be found in the larger kVA units.
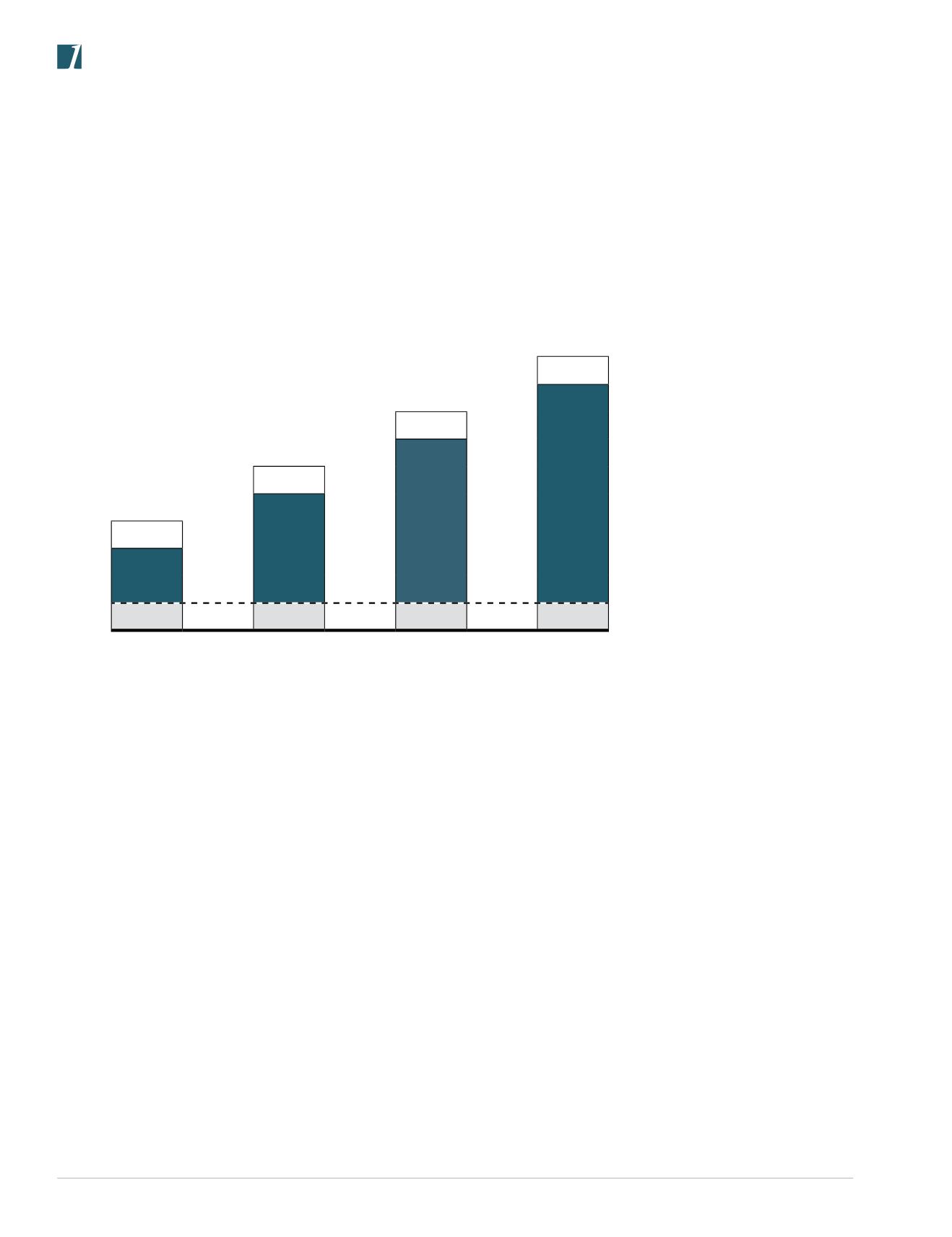
Referring to Figure A, small fractional kVA transformers use insulation class 130°C. Compound filled transformers use insulation
class 180°C. Larger ventilated transformers are designed to use 220°C insulation. All of these insulation systems will normally have
the same number of years operating life. A well designed transformer, observing these temperature limits, will have a life expectancy
of 20-25 years.
Total Winding Temperature
o
C
220
30
Coil Hot Spot Differential
180
150
Average Winding Rise
25
130
115
10
105
80
10
55
40
40
40
40
Ambient
AGENCY: UL/ANSI 1561 MARCH 1987
Figure A
17. Why should Dry-Type Transformers never be over-loaded?
Overloading of a transformer results in excessive temperature. This excessive temperature causes overheating which will result in
rapid deterioration of the insulation and cause complete failure of the transformer coils.
18. Are temperature rise and actual surface temperature related?
No. This can be compared with an ordinary light bulb. The filament temperature of a light bulb can exceed 2000 degrees, yet the
surface temperature of the bulb is low enough to permit touching with bare hands.
19. What is meant by “impedance” in transformers?
Impedance is the current limiting characteristic of a transformer and is expressed in percentage.
20. Why is impedance important?
It is used for determining the interrupting capacity of a circuit breaker or fuse employed to protect the primary of a transformer.
Example: Determine a minimum circuit breaker trip rating and interrupting capacity for a 10 kVA single phase transformer with 4%
impedance, to be operated from a 480 volt 60 Hz source.